
What Is 3D Printing?
3D printing is also known as additive manufacturing, or desktop fabrication. It is a process in which a real, physical object is created based on a 3D design blueprint. 3D printing is an emerging technology that first was introduced in the year 1986; however, it wasn’t until the 1990s that it began to draw serious attention from all corners of the technology world.
For many, 3D printing is no less than a technology right out of Star Trek or some parallel universe. The ability to create objects from the ground up is really astonishing for a great number of people.
How It Works
Contrary to traditional subtractive manufacturing processes that rely on methods of cutting and drilling to carve out objects, an additive manufacturing process like 3D printing works by ‘fusing together’ layers of powdered material to build an object.
This task is performed by a machine called a 3D printer which, under computer control, can carry out this process with unmatched precision and superior accuracy.
A typical modern 3D printer that creates objects based on the SLS process primarily works in the following manner. Here are some of the components and raw materials to give you an idea of how 3D printing works:
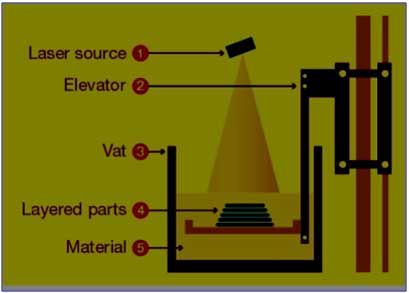
Laser Source
A laser is directed from the laser source to solidify and fuse together the molecules of a certain raw material.
Elevator
The Elevator is a component of a 3D printer that raises or lowers the platform to lay the layers of
the particular object that is being manufactured. Keep in mind that 3D printers create an object
layer-by-layer. Thus, the elevator helps in moving the object accordingly.
Vat
Think of the Vat as being a reservoir for the raw material.
Materials
Today’s advanced 3D printers are capable of using one or more types of raw materials for
creating objects. The materials that they can use include plastic, metals, resin and polymers.
Applications of 3D Printing
The rapid growth and improvements in 3D printing technology have enabled many industries to
benefit from it. Here are some of the industries that use 3D printing for a variety of purposes:
Aerospace – The technology is being used to manufacture complex yet light-weight parts for aircraft and space applications.
Architecture – This industry utilizes this technology for structure verification, design review, reverse-structure engineering, and expedited scaled modeling.
Automotive – The automotive industry actively uses 3D printing technology for design
verification as well as for the development of new engines.
Defense – 3D printing technology in the Defense sector is being utilized for making light-weight parts for surveillance equipment.
Education – 3D printing provides an excellent method for geometry visualizations and design initiatives at art schools. It is also used in numerous disciplines of study for research purposes.
Entertainment – All kinds of prototypes of toys, action figures, games, musical equipment and other things are being manufactured using 3D printers.
Healthcare – The medical field has gained an edge as a result of the advancements in 3D printing. A number of working organs have been created and a lot of research is being carried
out. It may not be too long when organs for transplant could be easily ‘printed’.
Manufacturing – The manufacturing industry employs the use of 3D printing for a variety of purposes, including creating models of products before they are manufactured on a mass scale. It is also used to achieve a faster product development cycle and for design troubleshooting.
Testimonials


